Energy Saving Opportunities
1. Thermocol (XPS Boards)

Function: Acts as a thermal insulating material.
Application:
Walls/Ceilings: Can be installed on the inside or outside to reduce heat flow.
Temperature Reduction: Provides up to 5°C reduction if applied on sun-facing walls/ceilings.
Installation:
Ceilings:
Terrace Floor: Over the deck installation.
False Ceiling: Under the deck installation.
Benefits: Saves electricity and enhances room aesthetics.
Walls:
Interior/Exterior: Can be installed without issues.
Finishing: Wall putty and paint can be applied for desired decor.
2. Wall Paint (White)
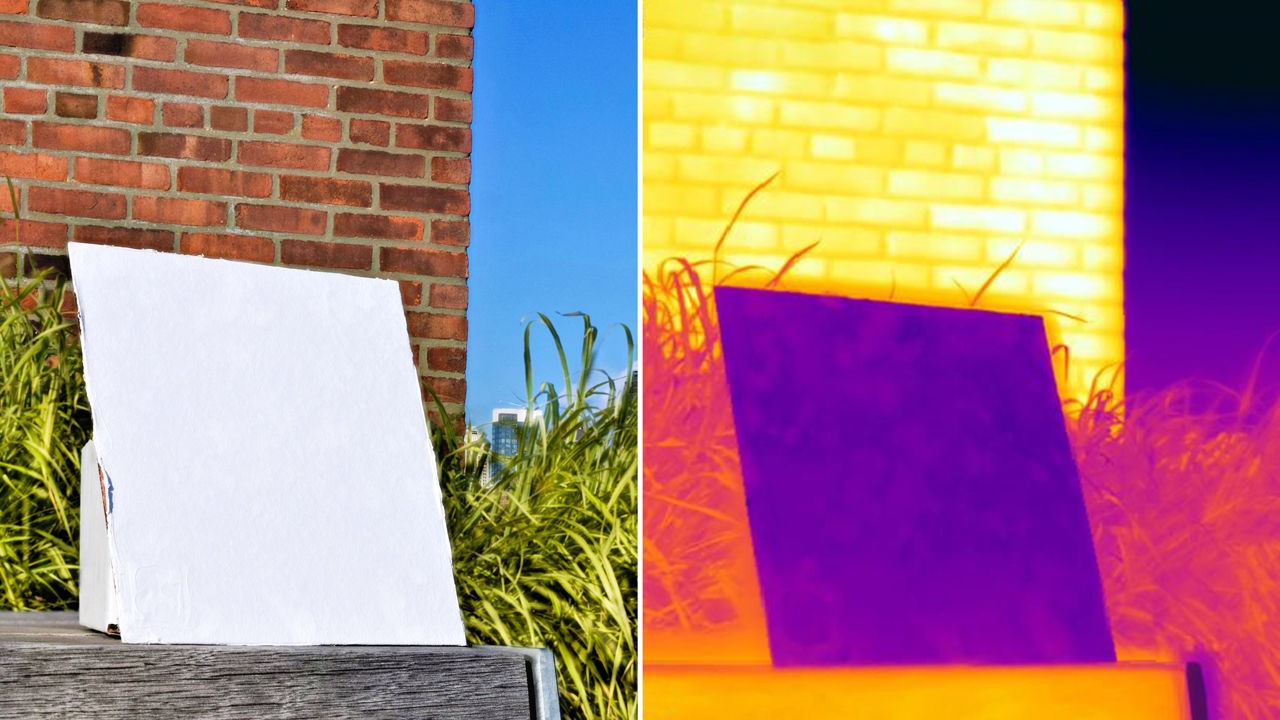

Function: Cooling technology that reduces indoor temperatures.
Features:
Temperature Reduction: Keeps surfaces up to 18°F cooler than ambient surroundings.
Energy Efficiency: Works like a refrigerator without energy consumption.
Environmental Impact: Reflects heat away from Earth into space, mitigating global warming.
3. Window Glass Pane
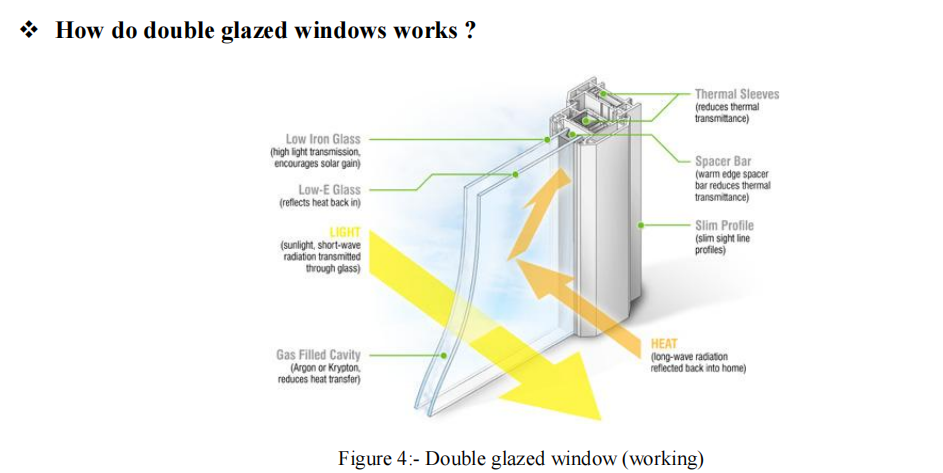
Definition: Glass fitted in window frames.
Types:
Single Glazing: Single glass pane.
Double Glazing: Two panes with an inert gas (like argon) between them for increased insulation.
Benefits:
Temperature Regulation: Effective in extreme weather conditions.
Noise Reduction: Insulates from outside noise.
Security: Difficult to break, enhancing security.
4. Insulation
Application Areas: Walls, roofs, floors.
Techniques:
Material: Insulation plates or foam can be used.
Cavity Walls: Hollow spaces in walls can be filled for better insulation.
Roof Types: Insulation methods differ for flat and steep roofs.
Floor Insulation: Specific to wood or concrete floors; soil insulation for crawl spaces.
Crack Sealing:
Purpose: Reduces heat loss by sealing cracks in the building shell.
Materials: Strips or other materials for windows, doors, and construction joints.
5. Voice Automated System

Function: Connects and controls devices through a centralized unit.
Devices: Lights, appliances, outlets, HVAC systems, alarms, doors, windows, smoke detectors, cameras, sensors.
Capabilities:
Automation: Schedule lights, adjust temperature, and trigger alarms.
Monitoring: Generate reports for efficient equipment usage.
Integration: Use AI systems like Google Home, Alexa, and Amazon Echo for IoT applications.
6. Building Management System (BMS)
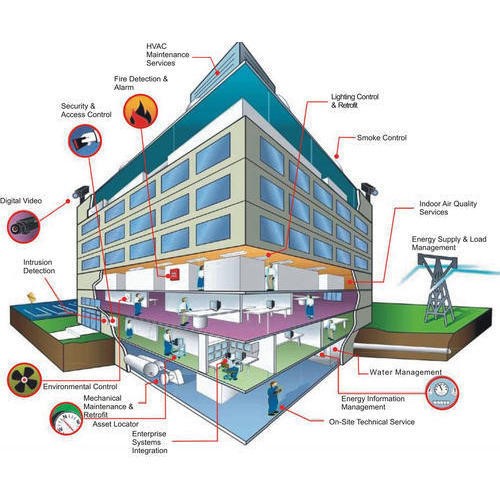
Definition: Computer-based system to control and monitor building electrical equipment.
Components: Software and hardware.
Benefits:
Energy Management: Reduces energy costs and optimizes comfort.
Remote Management: Controls HVAC systems remotely, saving maintenance time.
Applications: Essential for new builds to manage energy demand cost-effectively.